Unlike anything the world has ever seen before, Bitcoin appeared as a digital currency that has the potential to transform the concept of modern-day money and commerce by providing inexpensive, fast, and international money transfers, supporting promising internet currency. In 2009, Bitcoin started as a paper and a software project designed by Satoshi Nakamoto – an individual who seems to have been created to deliver Bitcoin to this world specifically.
Bitcoin initiated the crypto ecosystem, announcing to the world what it seems like to trade and transact with money concepts other than fiat currencies. Then, the world started adopting these cryptocurrencies, and the adoption grew only over the years.
Each nation has some reservations about regenerating their respective currencies. Some countries even go to print their currency in other nations, as Africa usually does in Europe. Here, the process of birthing cryptocurrencies is known as ‘Mining’. Basically, the Bitcoins we own do not come from above or some abstract events; a set of hardware and software components regenerates them.
This research will investigate the mining concept, analyze the process, and teach the hardware and software components.
What does it mean to mine Bitcoins?
Mining means the reproduction of the currency. It is the regeneration process by means of interacting with the Bitcoin network and working with high-processing mining machines to produce other bitcoins. From the early days of bitcoins, mining is the only way to obtain them as peer–to–peer trades are less trusted.
Just as ‘mining’ means extracting valuable materials from the earth, mining in the Bitcoin context is a set of activities aimed at verifying Bitcoin transactions, preventing double-spending, protecting the Bitcoin network, collecting transaction fees and, of course, extracting new Bitcoins. Getting new bitcoins is just seen as one of the reasons for mining. You might need to obtain bitcoins because you do not wish to exchange or sell. The reasons for mine can change along the way; as you learn more about bitcoins, you can choose to mine them for fun, science, commerce, and so on.
A miner, however, can be defined as the person who sets up mining computers and facilities (hardware), the hardware that works on extracting new bitcoins, or the software that executes the mining logic. In this paper, the three definitions will be used interchangeably.
“Bitcoin mining can be modelled as a conversion of electricity to heat. The cost of mining is dependent on energy efficiency, electricity pricing, the cost to exhaust heat, and sunken costs such as new infrastructure and labour. Bitcoin mining can be expanded in a more distributed and cost-effective manner through widespread access to variable electricity pricing schemes and hardware setups small enough not to require additional infrastructure.”
– Jonathan Harvey-Buschel
Mining verifies Bitcoin transactions by checking if they have occurred before. Transactions must send Bitcoins to valid Bitcoin addresses. They cannot spend non-existing bitcoins. When a miner detects a new valid block, he installs a new address to which mined bitcoins are awarded. Most miners take calculated risks; they put mining hardware to work, pay for electricity and make their profits by selling the rewarded bitcoins.
To understand more about Bitcoin mining facilities, several terms need to be understood. Some of them are:
• Hash: Hash is a mathematical function used to unify information
• Hash boards: An aluminium box with two fans that contains a controller and a few computing cards.
• Hash rate: The hash rate is the number of calculations per second when computing to solve mining problems.
• Mining Rig: A set of mining hardware devices used to mine with high power and efficiency.
• Node: A computer connected to a blockchain network.
• Transaction Fee: A transaction fee is an amount paid to a miner as an incentive for finding a valid block.
• Clock Speed: The speed at which a computer processor runs.
• Overclocking: Squeezing out/Increasing the clock speed from the processor.
• Underclocking: Lowering the clock speed of the graphics card.
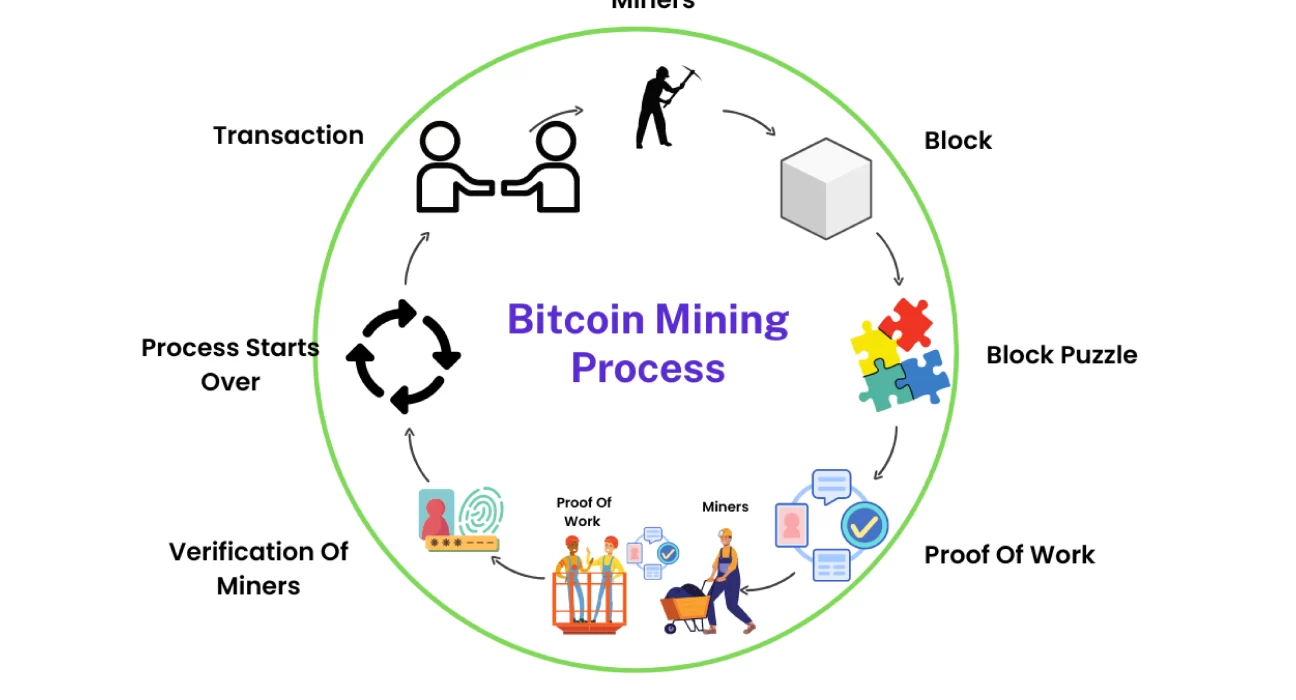
The Mining Process
To create new bitcoins, you need first to find a valid block. Blocks are structures, like a ledger, where data of transactions within the blockchain are permanently stored. You build a list of recent transactions and draft out some information about the proposed block; this summary is used to create a block header, combined with the nonce, the number only used once.
From the block header, the computers in the Bitcoin network then struggle to solve a compound math problem to deduce the hash – the hash itself is like a function that holds the security demand of the database; it is a combination of 64 characters. If the hash is enough to win at the 10-min frequency rate difficulty, then it is a winning block, and if otherwise, the nonce is changed, a new hash is calculated, and the process is tested again.
The process of trying out different nonces until one of them succeeds is called brutal force. Brutal force search is the only way to create a valid block. Therefore, the more your hardware processing power, the faster they can search, and you will be more likely to find a winning block.
So, the result (block generated) is shared and authenticated by other network nodes, and it will be added to the blockchain once verified. Upon this success, mining rewards are shared, in bitcoins, to the new address allocated to the new valid block created. As a miner, you clear bills of hardware with the awarded bitcoins. Since you might not want to risk too much without enough knowledge, consider an expert mining individual to do the whole process for you.
There is a process for the number of bitcoins given on a valid block. In 2012, 50 bitcoins were added once each miner’s block was valid. Then, it became 50% reduced in an event known as halving. Halving events occur every four years, and each time, there is a 50% reduction in the incentive. As of November 2021, it was reduced to 6.25 bitcoins, and that is the price till the next estimated halving date: April 12, 2024.